By Elana B. Multi award-winning writer, advertiser, speaker and internationally published author
What Metabolism is NOT
Trying to lose weight can be frustrating and to some people it can be downright depressing as they jump from one fad diet to the next. One problem is the misconception about metabolism. Many people believe the metabolism refers to the rate at which the body burns calories. However, this confusion is NOT metabolism. Understanding metabolism versus basal metabolic rate (BMR) is important in helping each individual’s journey with weight management and overall health. So what is the difference?
- BMR can increase based on the amount of muscle versus fat your body contains.
- Metabolism refers to the process by which the cells are able to break down food nutrients into energy to fuel various and necessary bodily functions—including thyroid, heart rate, digestion, breathing, circulation and so on.
What Is Metabolism?
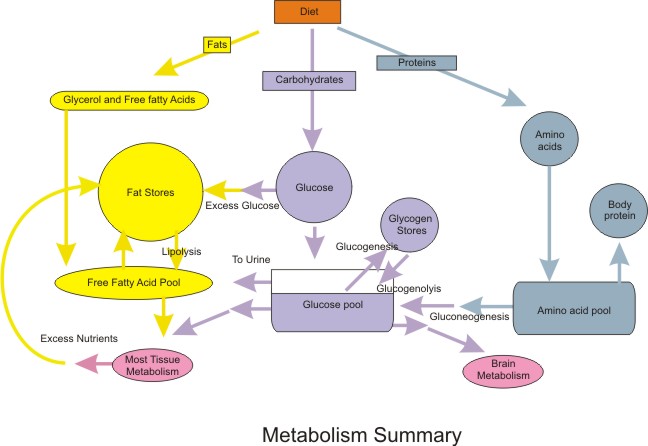
Metabolism refers to all the chemical reactions taking place in the body to convert or use energy. A few major examples of metabolism include:
• The breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins and fats in food to release energy.
• Transforming excess nitrogen into waste products excreted in urine.
• Breaking down or converting chemicals into other substances and transporting them inside cells.
So what is the key to metabolism?
Nutrition is the key. The pathways of metabolism rely upon nutrients that they breakdown in order to produce energy. Without energy we do not exist. Think of your body as a battery. Your body must stay charged (energized) to function. Energy formation is one of the vital components of metabolism. This energy is required by the body to synthesize new proteins, nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and to keep your body working. If you want your body to run like a Porsche, a Mercedes, a sturdy and long-lasting hybrid, take care of your nutrition and metabolic functioning and it will.
Metabolism can be conveniently divided into two categories
Anabolism – the synthesis of all compounds needed by the cells.
Catabolism – the breakdown of molecules to obtain energy.
What is the difference between Anabolism and Catabolism?
Both anabolism and catabolism are metabolic processes, but the two are contrasting from each other.
Catabolism produces energy
Anabolism uses energy
In the catabolic pathways, the large molecules are broken down into small monomers. In anabolism, small molecules are connected with each other, to form large molecules.
Catabolism is independent of anabolism. However, anabolism requires the ATP produced via catabolism.
Catabolism is functional at a higher rate during an activity, which needs energy to contract muscles, while anabolism is more functional during sleeping or resting.
Catabolic processes tend towards using up the stored food to produce energy, while anabolic processes likely to form, repair, and furnish the tissues and organs.
Essential nutrients supply energy (calories) and supply the necessary chemicals which the body itself cannot synthesize. Everything you do, including sleeping, waking, eating, sports, reading, even daydreaming, is fueled by energy produced from the calories you ingest. Water, your body’s most important nutrient, helps facilitate the chemical reactions that produce energy from food.
The diet needs essential nutrients like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and other inorganic elements.
The major elements are supplied in:
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Protein
Also necessary are:
Minerals
Vitamins
Water
How do carbohydrates work in metabolism?
Most people consume around half of their diet as carbohydrates. This comes in the form of rice, wheat, bread, potatoes, pasta, macaroni, etc. Carbohydrates include complex carbohydrates, starches, and simple sugars such as white sugar, high fructose corn syrup and honey. Choose 100-percent whole grains, and fruits and vegetables for most of your carbohydrates and you will add a good amount of fiber to your diet.
[adinserter block=”11″]
Foods supply carbohydrates in three forms:
- Starch: Starches form major sources of energy
- Sugar: Sugars for major and essential sources of energy
- Cellulose (fiber): Fibers contribute to bulk in the diet
Body tissues depend on glucose for all activities. Carbohydrates and sugars yield glucose by digestion or metabolism.
So which carbs are best?
Carbohydrates are found mostly in foods of plant origin—fruits and vegetables, which are a great source of complex carbs; however, carbohydrates also include whole grain products, sugars and starches. Try to avoid simple carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates are better than simple carbohydrates due to the large amount of vitamins, minerals and fiber they contain.
Whole grains contain the B vitamins, Vitamin E, zinc and magnesium. With these added nutrients involved, research has shown that they help to reduce the risk of heart disease and in some cases, they help with some cancers.
The other major benefit of complex carbs
• Prolonged energy. They are slow to digest so they will supply energy for a much longer time period than simple sugar which digests very quickly.
• The fiber content will help you feel full longer to control your appetite as well as maintain a healthy GI (gastrointestinal) tract.
• Fiber slows down the movement of food through the small intestine which helps increase the absorption of vitamins and minerals.
• When eating complex carbohydrates such as fruits and vegetables, be certain to eat from all of the different colors to get the full benefit of antioxidants and healthy fats as well.
Examples of the many colorful, antioxidant-rich complex carbs include:
GREEN
Asparagus
Avocado
Broccoli
Celery
Kale
Peas
Kiwi
Cabbage
BLUE / PURPLE
Beets
Purple cabbage
Black grapes
Blueberries
Plums
Figs
YELLOW/ORANGE
Apricots
Carrots
Grapefruit
Lemons
Peaches
Pumpkin and pumpkin seeds
Oranges
RED
Apples
Lima beans
Potatoes
Radishes
Raspberries
Red pepper (chili and bell peppers)
Tomatoes
WHITE
Banana
Garlic
Mushroom
Onion
Shallots
Turnips
Eating a good balance between whole grains, fruits and vegetables will give you all the vitamins and nutrients, fiber, and prolonged energy sources you will need for a healthy diet.
Best complex carb sources from grains:
Barley
Beans
Brown Rice
Oatmeal
Quinoa
Whole rye or wheat breads and pasta
Sprouted grains
Proteins in metabolism
- Proteins are the main tissue builders in the body. So what benefits do proteins have? Proteins are part of every cell in the body.
- Proteins help in cell structure, functions, and hemoglobin formation to carry oxygen, enzymes to carry out vital reactions and a myriad of other functions in the body.
- Proteins are also vital in supplying nitrogen for DNA and RNA genetic material and energy production. Proteins are also necessary for nutrition.
Protein contains 20 amino acids; however, the human body is unable to synthesize 8 “essential amino acids.”
Due to the human body’s inability to synthesize 8 essential amino acids, we need to add foods that are rich in these essential amino acids to our daily diet.
[adinserter block=”12″]
The essential amino acids that the body is unable to synthesize include:
Isoleucine
Leucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Threonine
Tryptophan
Valine
Minerals and vitamins in metabolism
The minerals in foods do not contribute directly to energy needs but are important as body regulators and play a role in metabolic pathways of the body. More than 50 elements are found in the human body; of those, about 25 elements have been found to be essential. A shortage of these minerals and vitamins can create symptomatic deficiencies in the body, which can be seen in illnesses, general malaise, and in some cases diseases, such as: scurvy, rickets, beriberi and pellagra.
Important minerals for the human body include:
calcium
phosphorus
iron
sodium
potassium
chloride ions
copper
cobalt
manganese
zinc
magnesium
fluorine
iodine
Vitamins are essential organic compounds that the human body cannot synthesize by itself and must therefore, be present in the diet.
Vitamins particularly important in metabolism include:
Vitamin A
B2 (riboflavin)
Niacin or nicotinic acid
Pantothenic Acid
Needed fats in metabolism
• Fats are concentrated sources of energy.
• Fats produce twice the energy as either carbohydrates or protein on a weight basis.
• Fats help to form cellular structure and form a protective cushion and insulation around our vital organs.
What else do healthy fats do?
The function of healthy fats also include:
- Help absorbing fat soluble vitamins.
- Providing reserve storage for energy (that’s why you don’t want an overload…too much fat and the body can not store it properly.
- Extra fat particles wreak havoc on and inside the arteries.
Essential fatty acids include unsaturated fatty acids that need to be in the diet, such as:
Linoleic acid
Linolinic acid
Arachidonic acid
Saturated fats, along with cholesterol, have been implicated in arteriosclerosis and heart disease. These saturated fats that are high in low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which is the bad kind of cholesterol, and should be avoided.
What to avoid
Avoid sugary snacks, pastries, sugar-sweetened soft drinks, candy, and cookies. Most processed foods (especially boxed) contain added sugars, even those that don’t taste sweet. These foods usually have too many calories, and are loaded with trans fats, simple (no value) sugars and generally offer little or no nutritional value, most work against a healthy diet.
Balance your carbohydrate choices with protein sources such as lean meat, poultry, eggs, or fish, and some healthy fat such as organic coconut oil (which is good for you raw and is safe to cook with) or organic, extra-virgin olive oil (which is safe to cook with at low levels and small amounts are good with herbs for salad dressings) avocado or nuts and seeds. Protein combined with high-fiber carbs helps keep you feel full between meals.
How to boost your metabolism to stay fit
Foods that help:
Egg whites are a great way to boost your metabolism.
•They are filled with amino acids and keep your metabolism burning
•They are full of protein.
Lean meat
• Keeps your metabolism going so you can burn fat throughout the day
• Is full of iron, which is great for you.
Water
• Is so important to hydrate to keep your metabolism boosted.
• You should drink up to ½ of your body weight in ounces a day.
Coffee
• Can boost your metabolic rate.
• Drinking coffee (with caffeine) can help you burn more, especially before a workout.
• If you have anxiety or are easily stressed or agitated, coffee may aggravate your condition and possibly give you insomnia.
Green tea
• Promotes fat-burning.
Whole grains
• Helps burn fat throughout the day.
• Are filled with fiber.
• Whole grains help boost your metabolism.
Vegetables
• Low in calories yet high in fiber.
• Fiber makes you feel full.
• Certain vegetables contain nutrients that boost your metabolism.
• Leafy green vegetables like spinach, kale, turnip greens and collard greens are rich in iron, which help boost your metabolism.
Lentils
• The body needs a proper amount of iron in order to burn fat.
• Eat up to one cup of lentils every day to get your daily iron needs.
What if you have tried everything and you are exhausted emotionally and physically and still feel out of shape? Make sure your thyroid is functioning properly. If your thyroid is out of whack, so to speak, your whole body can be thrown into a conundrum.
Proper thyroid function through either natural supplementation or medications will be necessary to bring your body into proper functioning. Nutrition and exercise are key factors in proper thyroid function; however, as we age, so does the ability for some of our bodily functions to operate at their optimum levels.
So why isn’t this considered the KEY to metabolism?
The Key is to the door. The door opens the house. The “thyroid” is the house in this equation. The door (your mouth) is blocked until nutrition is correct and the body is functioning properly. If some other imbalance in your body is causing the door to be blocked, it is not something external such as the food that you eat and the physical activity you participate in or the lack thereof. The problem stems from internal sources. You need to treat the problem and not just the obvious symptoms.
If you are exercising on a daily basis and eating a healthy organic (non GMO, no insecticides, or growth hormone foods) and you still can not get your body and metabolism functioning properly, this, more than likely, is due to your thyroid.
Consult your doctor before using any health treatment, plan, or activity — including herbal supplements and natural remedies — and tell your doctor if you have a serious medical condition or are taking any medications. The information presented here is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as substitute for medical advice or counseling.
About the author: Elana B. is a multi award-winning writer, speaker, and internationally published author. As a writer and ghostwriter she has written hundreds of stories from shorts to books to screenplays.
A gifted storyteller, Elana B.’s new children’s series, Too Terribly Busy and the “Too Terribly” Series of books, teach in a fun, creative way some of the most important lessons in life. Through this entertaining series of books, children will learn morals, manners, how important it is to achieve goals, as well as conflict resolution. Sneak peek of the first story in the new series: TooTerriblyBusy-SP1.
More by Elana B. and other related articles:
Signs of Depression and How to Feel Good Again
30 Minutes of Physical Activity
The Feel Good Way to Better Health…Endorphins
Medical Conditions and Triglycerides
5 Tips to Help Improve Relationships
Natural Ways to Reduce High Blood Pressure
Lowering Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
Heart Disease – The Ticking Time Bomb
Other great articles:
The Writer’s Life and How to Make Money as a Writer






